Requirements for prescribing and administering medicines
Adam La Caze
Semester 2, 2019
Background
Objectives (Overall)
- Understand the purpose and contents of the HDPR in the context of nursing and midwifery practice
- Be able to navigate the HDPR
- Be able to determine how a medicine needs to be prescribed, dispensed and administered to be in accordance with the law.
This section of the module…
Here we focus on Objective 3
Be able to determine how a medicine needs to be prescribed, dispensed and administered to be in accordance with the law..
First, we focus on prescribing and prescriptions
Key concepts
- The HDPR endorses a number of professions to prescribe.
- Non-medical prescribers are regulated in a number of different ways.
- Key regulations regarding prescriptions: s79 and s190
- There are different types of prescription that are regulated in slightly different ways: handwritten, computer generated and electronic
- Restricted medicines and controlled medicines have slightly different requirements in relation to how they are stored and what records need to be kept
Endorsement to prescribe
Medical and non-medical prescribing
A number of professions are endorsed to prescribe.
Non-medical prescribers are more tightly regulated than medical prescribers.
Contrast s58 with s56 and s67(4)
Regulating non-medical prescribing
There are two main ways that non-medical prescribing is regulated in the HDPR
- Endorse members of the profession to prescribe a restricted formulary, and/or
- Endorse some members of a profession who have demonstrated specific knowledge and skills to prescribe in specified circumstances (within an individual’s scope of practice)
Dentists are endorsed to prescribe a restricted formulary of controlled drugs (s56).
Nurse Practitioners are endorsed to prescribe controlled drugs within their scope of practice (s62B).
Drug therapy protocol
- Drug therapy protocol (Appendix 9)
- means a certified document published by the department stating circumstances in which, and conditions under which, a person who may act under the protocol may use a stated controlled or restricted drug or poison for stated purposes
The drug therapy protocols discussed in the HDPR are published on the Queensland Health website.
Have a look at the Drug therapy protocols for Midwives
Prescribing within a scope of practice
Until November 2018, nurse practitioners were also required to prescribe according to a Drug Therapy Protocol.
This requirement was removed from nurse practitioners, and a new category of midwives—endorsed midwives—was recognised in the HDPR. Both of these groups are endorsed to prescribe within their scope of practice.
Prescriptions
Types of prescriptions
The HDPR refers to two types of prescriptions: paper prescriptions and electronic prescriptions
Look up the definitions in Appendix 9
Electronic prescriptions
Electronic prescriptions are becoming more common, and happen now in some hospitals and nursing homes.
Electronic prescriptions are also being used in community settings—but at the moment in Queensland they are used as a supplement to paper prescriptions.
Prescription Exchange Services include: eRx and medisecure.
Paper prescriptions
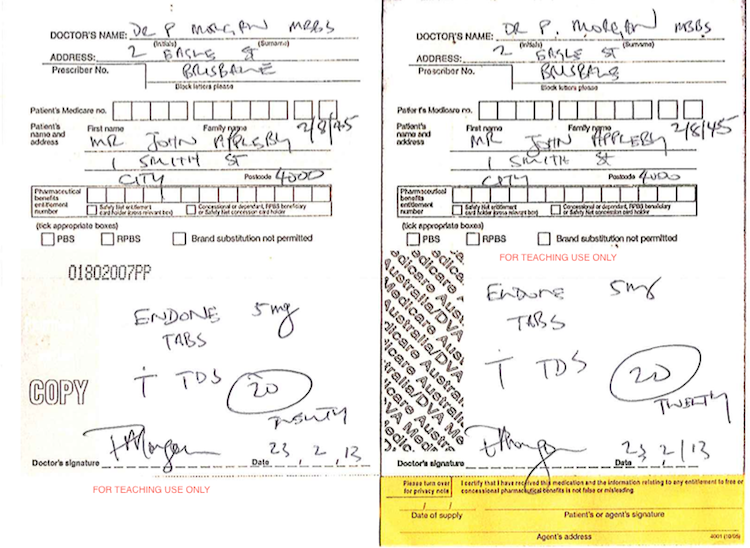
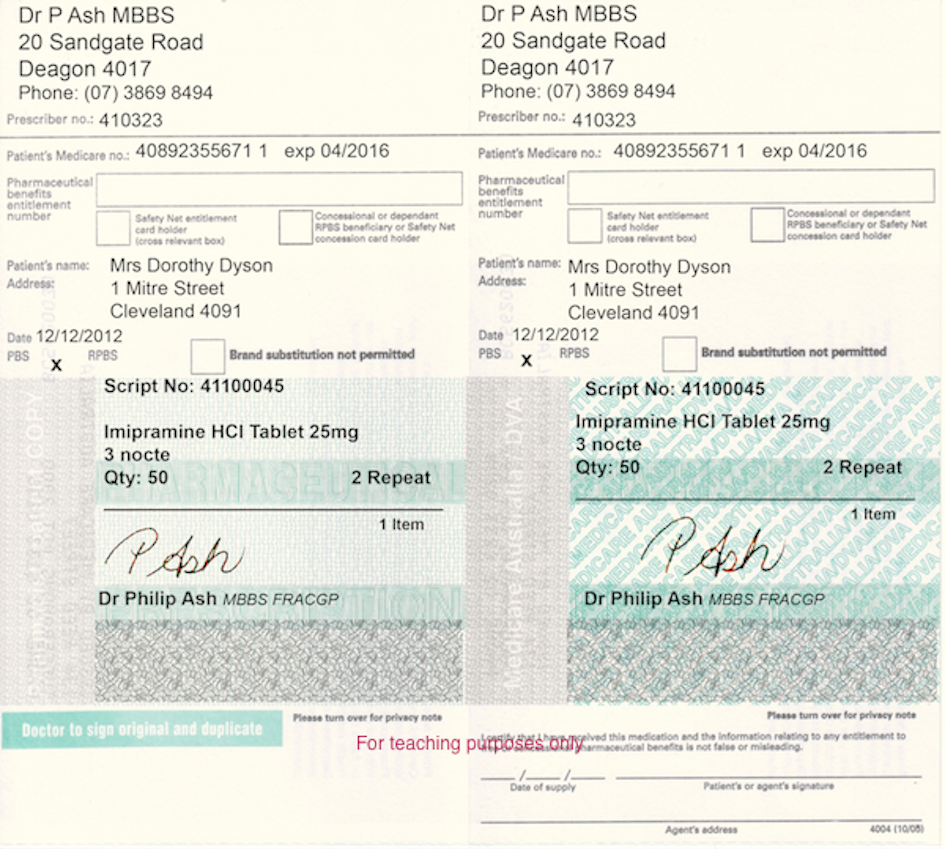
There are two types of paper prescriptions: hand written prescriptions and computer generated prescriptions. (Both examples are modified slightly for teaching purposes).
Regulations on prescriptions
The key regulations are s79 for controlled drugs and s190 for restricted drugs.
s79 (controlled drugs) and s190 (restricted drugs) are very similar, but there are important differences.
See for example: s79(4)(e), and contrast s79(4)(c) with s190(2)(c)
Records and storage of medicines
Storing medicines
The HDPR regulates the ways in which medicines are stored in institutions and units/wards.
Storage requirements depend on the scheduling of the medicine.
What are the general storage requirements of restricted and controlled medicines? (Compare s119 with s211)
Records for obtaining and administering controlled drugs
There are additional recording requirements for controlled drugs to the risk of misadventure with these drugs.
Records of the controlled drug need to be made when the controlled drug enters the ward (or unit) and when it is administered.
s103 provides the recording requirements when administering controlled drugs in a unit or ward.
What is the difference between s103 and s109?
Summary
This completes the module. Test your knowledge on this section of the module in the associated quiz.
Space, Right Arrow or swipe left to move to next slide, click help below for more details